Dry Eye: Accutane
HOW ACCUTANE CAUSES DRY EYE
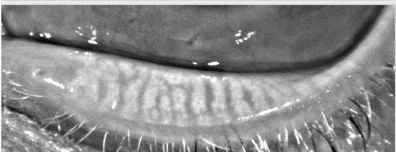
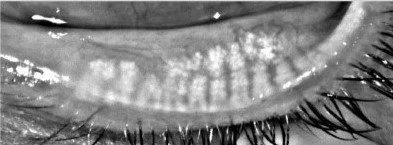
Isotretinoin’s mechanism of action is to suppress sebum production. The general consensus is that the medication affects the meibomian glands in a similar fashion to its effects on the sebaceous glands of the skin. By altering the meibomian gland function, there is a decrease in the production of tear film lipid layer, which in turn increases tear evaporation. The dysregulation of tear film quality and quantity can lead to dry eye disease and in some cases lead to corneal nerve de-sensitivity. Roughly 50% of patients experience dry eye symptoms while on the medication, but the long-term consequences of meibomian gland function have yet to be studied.
Our optometrists recommend an evaluation prior to taking the medication to gather baseline testing which can then be monitored once the medication is discontinued. Patients with a history of Accutane use who are now wearing contact lenses and/or considering refractive laser eye surgery, should receive a comprehensive eye examination with an emphasis on meibomian gland and corneal health.
Learn more about meibomian gland dysfunction treatments by clicking here!
Meibomian Gland prior to Accutane
Meibomian Gland atrophy after Accutane use
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING:
Tear osmolarity
Anterior segment examination
LashCamTM
Meibomian Gland Evaluator
TREATMENT:
Based on the results and severity of meibomian gland dysfunction, a customized treatment plan may include warm compresses, omega 3 and/or gamma linoleic acid supplements, lid hygiene, expression of meibomian glands and Blephex treatment.
Heated mask compresses
Tea tree oil cleansers
Preservative-free artificial tears
Omega 3 / GLA supplements
Meibomian gland expression
Lid exfoliation